Natazia®: A low-dose OC that delivers high
contraceptive efficacy3
Natazia®: A low-dose OC that delivers high
contraceptive efficacy3
For pregnancy prevention and the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) in women without organic pathology who choose to use an oral contraceptive (OC) as their method of contraception1
Highly effective in pregnancy prevention
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Natazia must be taken exactly as directed.


The Pearl Index (PI) was the primary efficacy endpoint used to assess contraceptive reliability and was assessed in each of the 2 studies, assuming all subjects were at risk of pregnancy in all medication cycles unless backup contraception was documented. The PI is based on pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment and within 7 days after the last pill intake. Cycles in which conception did not occur, but which included the use of backup contraception, were not included in the calculation of the PI. The PI also includes patients who did not take the drug correctly. The Kaplan-Meier method was also used to calculate the contraceptive failure rate.
Study 1: A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, unintended pregnancy study conducted in the United States and Canada included 490 healthy subjects between 18 and 35 years of age (mean age: 25.1 years) who were treated for up to 28 cycles of 28 days each. The weight range for treated women was 40 kg to 100 kg (mean weight: 62.5 kg) and the body mass index (BMI) range was 14 kg/m2 to 30 kg/m2 (mean BMI: 23.3 kg/m2). Of treated women, 15% discontinued the study treatment due to an adverse event, 13% were lost to follow-up, 10% withdrew their consent, 8% discontinued due to other reasons, 1% discontinued due to protocol deviation, and 1% discontinued due to pregnancy.
Study 2: A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, contraceptive reliability study conducted in Europe (Germany, Austria, and Spain). There were 1377 healthy subjects between 18 and 50 years of age (mean age: 30.3 years) who were treated for 20 cycles of 28 days each. The weight range for treated women was 38 kg to 98 kg (mean weight: 63.8 kg) and the BMI range was 15 kg/m2 to 31.8 kg/m2 (mean BMI: 22.8 kg/m2). Of treated women, 10% discontinued the study treatment due to an adverse event, 5% discontinued due to other reasons, 2% were lost to follow-up, 2% discontinued due to protocol deviation, 2% withdrew their consent, and 1% discontinued due to pregnancy.
Common Adverse Reactions (≥2%) in contraception (n=1867) and HMB (n=264) studies:
Headache (including migraines) (12.7%), breast pain, discomfort, or tenderness (7.0%), menstrual disorders (metrorrhagia, menstruation irregular, menorrhagia, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, genital hemorrhage, abnormal withdrawal bleeding, uterine hemorrhage) (6.9%), nausea or vomiting (6.0%), acne (3.9%), mood changes (depression, mood swings, depressed mood, mood altered, affect lability, dysthymic disorder, crying) (3.0%), and increased weight (2.9%).
Demonstrated a shorter, lighter scheduled withdrawal bleed versus a monophasic 21/7 OC containing 20 mcg of ethinyl estradiol (EE) and 100 mcg of levonorgestrel (LNG)7
Study Design: A multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy, randomized clinical trial conducted in 34 centers in Germany, the Czech Republic, and France between March 2005 and September 2006. 804 healthy women aged 18 to 50 years were randomized to receive 28 days of either Natazia or a monophasic OC containing 20 mcg of EE and 100 mcg of LNG for 7 cycles. The dosing on the monophasic regimen was administered on days 1 to 21 with a placebo on days 22 to 28. Participants were assessed at screening (visit 1), baseline (visit 2), weeks 15 to 16 (visit 3), and at final examination from weeks 29 to 30 or at discontinuation (visit 4). The primary efficacy outcomes were bleeding pattern (number of bleeding/spotting days, as well as the number and length of bleeding/spotting episodes) and cycle control (incidence and characteristics of scheduled and intracyclic bleeding). Bleeding was assessed daily using diary cards. Bleeding intensity was gauged on a 5-point scale, where 1=none, 2=spotting, 3=light, 4=normal, and 5=heavy.7
This study was descriptive in nature and was not designed to show equivalence or noninferiority. 95% confidence intervals were calculated for bleeding/spotting per reference period. Post hoc statistical analyses were conducted in order to test for treatment differences in bleeding pattern and cycle control outcomes.7
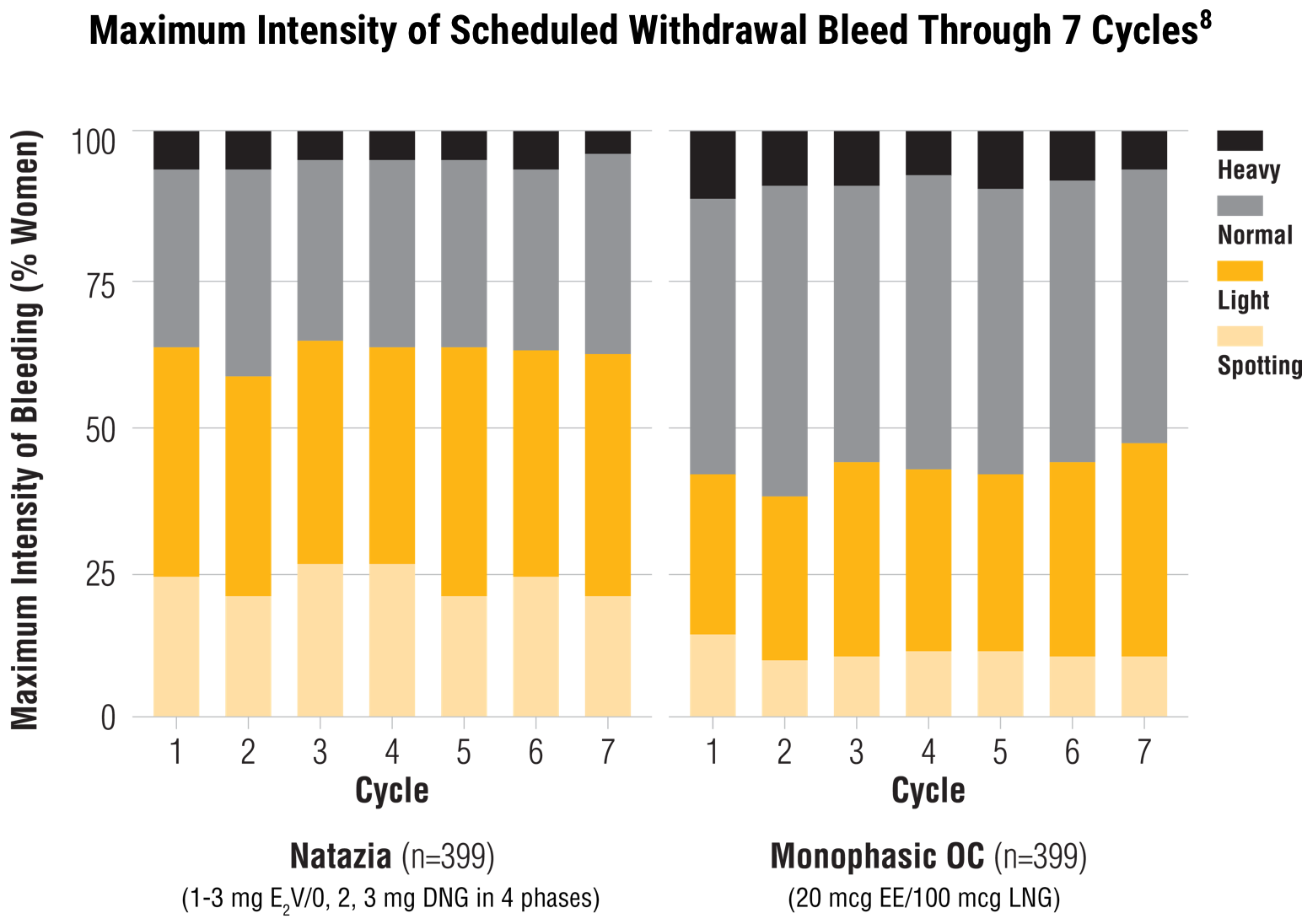
When compared with a monophasic OC, Natazia treatment resulted in:
Lower maximum intensity of withdrawal bleeding 7
Estradiol valerate/dienogest (E2V/DNG) median score 3 (light bleeding) versus EE/LNG median score 4 (normal bleeding)*
Shorter mean duration of withdrawal bleeding over 7 cycles7
E2V/DNG median 4.0 days versus EE/LNG median 5.0 days (P<0.05 per cycle)
*A greater proportion of women who received Natazia experienced spotting or light bleeding, relative to those who received the comparator.7
When compared with a monophasic OC, Natazia treatment resulted in:
Lower maximum intensity of withdrawal bleeding 7
Estradiol valerate/dienogest (E2V/DNG) median score 3 (light bleeding) versus EE/LNG median score 4 (normal bleeding)*
*A greater proportion of women who received Natazia experienced spotting or light bleeding, relative to those who received the comparator.7
Shorter mean duration of withdrawal bleeding over 7 cycles7
E2V/DNG median 4.0 days versus EE/LNG median 5.0 days (P<0.05 per cycle)
Fewer women experienced a scheduled withdrawal bleed with Natazia when compared with a monophasic OC containing 20 mcg of EE and 100 mcg of LNG7
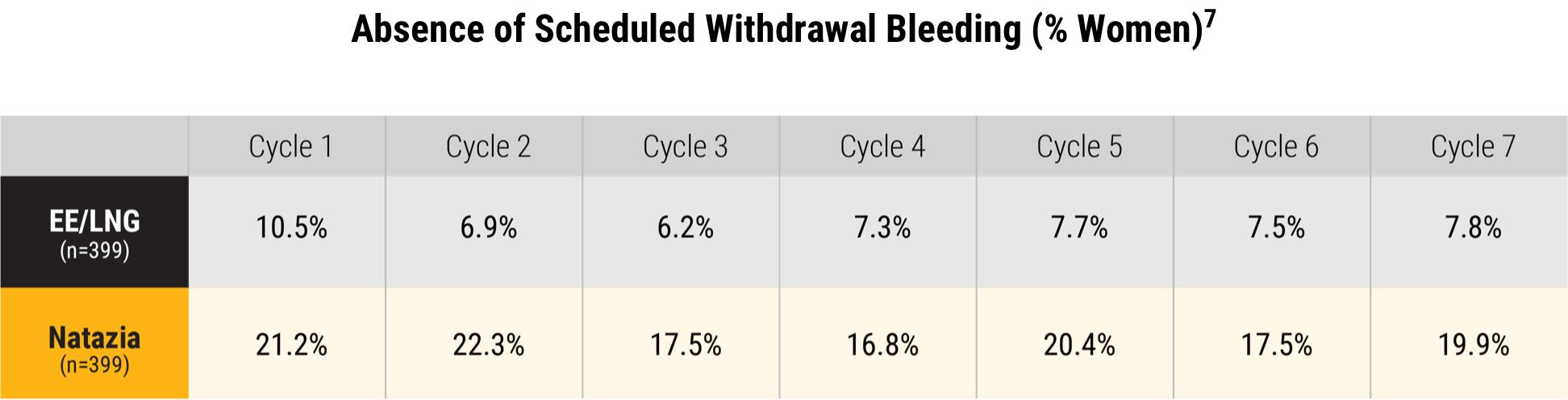
Smaller proportion of women who experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding per cycle 7
E2V/DNG range from 77.7% to 83.2% versus EE/LNG 89.5% to 93.8% (P<0.0001 in each cycle over 7 cycles)
Greater proportion of women with an absence of scheduled withdrawal bleeding over 7 cycles 7
Mean 19.4% over 7 cycles versus 7.7% for the comparator (P<0.0001 for all cycles)
Adverse events (AEs) considered possibly related to treatment occurred in 10% of women treated with E2V/DNG and 8.5% of women treated with EE/LNG. The most frequently reported AEs in women treated with E2V/DNG were breast pain (3.8%), headache (2.5%), and vaginal infection (2.5%), while those in women treated with EE/LNG were acne (3.3%), headache (3.3%), and nasopharyngitis (1.8%). The rate of discontinuation due to AEs was 3.3% in both treatment groups. No women discontinued due to bleeding disorders.7
Smaller proportion of women who experienced scheduled withdrawal bleeding per cycle 7
E2V/DNG range from 77.7% to 83.2% versus EE/LNG 89.5% to 93.8% (P<0.0001 in each cycle over 7 cycles)
Greater proportion of women with an absence of scheduled withdrawal bleeding over 7 cycles 7
Mean 19.4% over 7 cycles versus 7.7% for the comparator (P<0.0001 for all cycles)
Adverse events (AEs) considered possibly related to treatment occurred in 10% of women treated with E2V/DNG and 8.5% of women treated with EE/LNG. The most frequently reported AEs in women treated with E2V/DNG were breast pain (3.8%), headache (2.5%), and vaginal infection (2.5%), while those in women treated with EE/LNG were acne (3.3%), headache (3.3%), and nasopharyngitis (1.8%). The rate of discontinuation due to AEs was 3.3% in both treatment groups. No women discontinued due to bleeding disorders.7


