An OC that improves HMB symptoms and reduces menstrual blood loss9,10
For pregnancy prevention and the treatment of heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) in women without organic pathology who choose to use an oral contraceptive (OC) as their method of contraception1
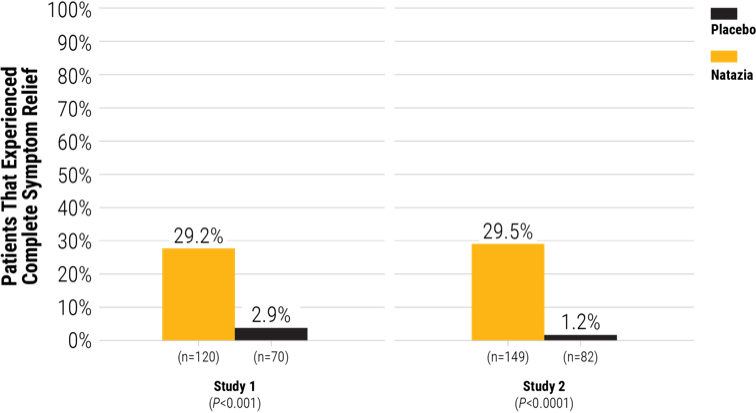
Significantly more women with HMB experienced complete symptom relief with Natazia® compared with placebo (intent to treat)9,10
Study Design: The efficacy and safety of Natazia were evaluated in 2 multiregional, multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials, which were identical in design. Study 1 was performed in the United States and Canada, and Study 2 was performed in Australia and 9 European countries. The studies enrolled women aged 18 years or older with a diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding characterized as heavy, prolonged, and/or frequent bleeding without organic pathology. The diagnosis of HMB was documented through the collection of used sanitary protection (pads and tampons) to quantify blood loss assessed by the alkaline hematin method. Overall, about 85% of the subjects qualified for the study because they had HMB symptoms. A total of 421 women (mean age: 38.2 years) and a mean body mass index (BMI) of 25.5 kg/m2 were randomized to the 2 clinical studies, for a total of 269 women in the Natazia group and 152 women in the placebo group. They were treated for seven 28-day cycles. Approximately 81% were Caucasian, 13% were Black, and 6% were Hispanic, Asian, or other.
The primary efficacy variable was the proportion of subjects who were completely relieved of symptoms. This was defined by:
-
The number of subjects with the absence of any dysfunctional bleeding symptom
-
Those who met up to 8 strictly defined criteria for success during the 90-day efficacy assessment phase
HMB was defined as menstrual blood loss (MBL) ≥80 mL in ≥2 bleeding episodes
Complete symptom relief was achieved by more women treated with Natazia compared with placebo9,10
Common Adverse Reactions (≥2%) in contraception (n=1867) and HMB (n=264) studies:
Headache (including migraines) (12.7%), breast pain, discomfort, or tenderness (7.0%), menstrual disorders (metrorrhagia, menstruation irregular, menorrhagia, vaginal hemorrhage, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, genital hemorrhage, abnormal withdrawal bleeding, uterine hemorrhage) (6.9%), nausea or vomiting (6.0%), acne (3.9%), mood changes (depression, mood swings, depressed mood, mood altered, affect lability, dysthymic disorder, crying) (3.0%), and increased weight (2.9%).
What is HMB?
HMB was defined as MBL of 80 mL or more in at least 2 bleeding episodes. The diagnosis of HMB was documented through the collection of used sanitary protection (pads and tampons) to quantify blood loss assessed by the alkaline hematin method. Overall, about 85% of the subjects qualified for the study because they had HMB symptoms.
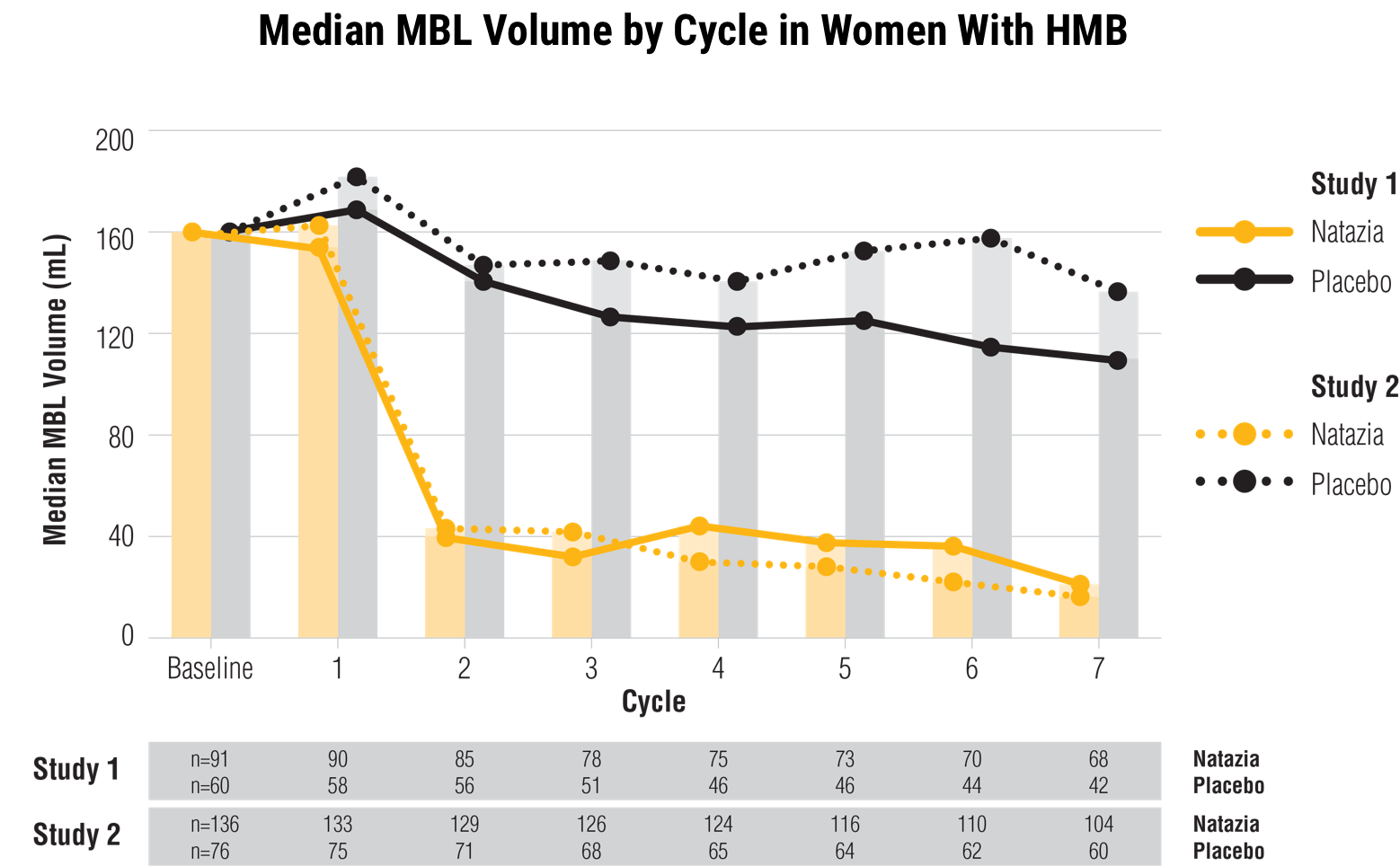
Natazia significantly reduced median menstrual blood loss in women with HMB versus placebo at cycle 7
In 2 studies, women with HMB taking Natazia experienced a statistically significant reduction in median menstrual blood volume (MBV) at cycle 7 from baseline compared with placebo (P<0.0001 for both studies)
Serious Adverse Reactions in contraception (n=1867) and HMB (n=264) studies:
Myocardial infarction (2 cases), ruptured ovarian cyst (2 cases), deep vein thrombosis, focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver, uterine leiomyoma, acute cholecystitis, and chronic acalculous cholecystitis.


